Positive advantages of fruits have been well-known by many people. Fruits can make you healthy and beautiful. One of them are banana. This yellow fruit is eatable for all ages from a baby until a grandmother and grandfather. But what can a banana do actually for our body? The following notes are 10 interesting facts about banana nutrition that might be we do not know.
1. Banana can make you happy.
Bananas contain a substance that can help the brain produce 5-HT. This substance helps dismiss irritable emotions and pessimism. Europeans usually call this fruit as a happy fruit that can lift depression.
2. Slimming your body.
Bananas are also good for loosing your weight because they are rich in nutrition and calories and also free of sodium, fat and cholesterol. In addition, no other fruits contain more digestible carbohydrates than bananas. This is advantageous because the body burns off calories from carbohydrate more easily and quickly than calories from fat or protein.
3. Preventing you from heart disease and high blood pressure.
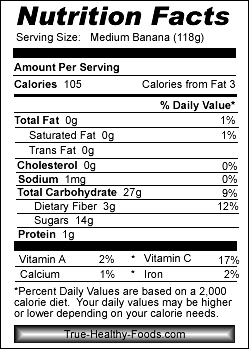
Bananas contain good amounts of health benefiting anti-oxidants, minerals, and vitamins that can help prevent heart disease and lower high blood pressure. Fresh banana provides 358 mg potassium per 100 g of fruit. Potassium helps control heart rate and blood pressure, countering bad effects of sodium. It also reduces the risk of hypertension and stroke. In addition, research has shown that potassium in a banana boost students brain power who are eating banana at a breakfast, break, and lunch so that they are more alert in the class.
4. Treating constipation.
The fruit contains soluble dietary fiber (7% of DRA per 100 g) that helps normal bowel movements; thereby reducing constipation problems.
5. Good for those who are hard to sleep well.
A banana contains protein and amino acids which are effective in treating insomnia or emotional stress. The protein and amino acids can calm the nerves that makes bananas are good for those who are hard to sleep well.
6. Containing three separate sugars.
Bananas contain three natural sugars. Those are sucrose, fructose and glucose along with fiber that make a banana gives an instant and substantial boost of energy. Therefore, for this quality, bananas are being used by athletes to get instant energy and as supplement food in the treatment plan for underweight children.
7. Curing diarrhea.
If you have a diarrhea, try to eat a ripe banana. It normalizes colonic functions in the large intestine by absorbing large amounts of water and helps regulate proper bowel movements.
8. Helping our body to defend and heal against infections.
Bananas are also rich in Vitamin C (about 8.7 mg per 100g). This vitamins that helps our body to defend and heal against infections. In addition, it also proves valuable in the synthesis of the connective tissue, absorption of iron and the formation of blood. Beside vitamin C, this fruit is also rich in vitamin B-6 (pyridoxine) which is an important B-complex vitamin that has beneficial role in the treatment of neuritis, anemia, and decreasing homocystine (one of the causative factor for coronary artery disease (CHD) and stroke episodes) levels in the body.
9. Slowing down the aging and various disease processes.
Oxygen-derived free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS) are the agents that play a role in aging and various disease processes. And bananas contain many health promoting flavonoid poly-phenolic antioxidants such as lutein, zeaxanthin, beta and alpha carotenes in small amounts which help act as protective hunter against those agents.
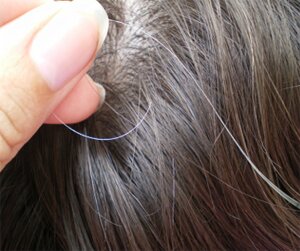
10. Preventing graying hair and pigmentation.
Bananas contain chromium, fluoride, manganese, and zinc. And Along with all above, this fruit also contains plenty amounts of copper that is good in preventing graying your hair and also selenium to prevent pigmentation. What an amazing fruit, isn’t it?
Those are nutrition inside the yellow cover of the fruit. Those facts are just 10 of many banana nutrition facts that can be shared from many sources. So, enjoy the fruit.







 www.PortlandPayday.Loans
www.PortlandPayday.Loans
Worldwide, there is no sharp distinction between “bananas” and “plantains”. Especially in the Americas and Europe, “banana” usually refers to soft, sweet, dessert bananas, particularly those of the Cavendish group, which are the main exports from banana-growing countries. By contrast, Musa cultivars with firmer, starchier fruit are called “plantains”. In other regions, such as Southeast Asia, many more kinds of banana are grown and eaten, so the simple two-fold distinction is not useful and is not made in local languages.:
Southeast Asian farmers first domesticated bananas. Recent archaeological and palaeoenvironmental evidence at Kuk Swamp in the Western Highlands Province of Papua New Guinea suggests that banana cultivation there goes back to at least 5000 BCE, and possibly to 8000 BCE.,..’;